{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"___\n",
"\n",
" \n",
"___\n",
"Copyright Pierian Data\n",
"For more information, visit us at www.pieriandata.com"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"collapsed": true
},
"source": [
"# NumPy Operations"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Arithmetic\n",
"\n",
"You can easily perform *array with array* arithmetic, or *scalar with array* arithmetic. Let's see some examples:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 1,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])"
]
},
"execution_count": 1,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"import numpy as np\n",
"arr = np.arange(0,10)\n",
"arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 2,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([ 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18])"
]
},
"execution_count": 2,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr + arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 3,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([ 0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81])"
]
},
"execution_count": 3,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr * arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 4,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])"
]
},
"execution_count": 4,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr - arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 5,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stderr",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"C:\\Anaconda3\\envs\\tsa_course\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:3: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in true_divide\n",
" This is separate from the ipykernel package so we can avoid doing imports until\n"
]
},
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([nan, 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])"
]
},
"execution_count": 5,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"# This will raise a Warning on division by zero, but not an error!\n",
"# It just fills the spot with nan\n",
"arr/arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 6,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stderr",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"C:\\Anaconda3\\envs\\tsa_course\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:2: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in true_divide\n",
" \n"
]
},
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([ inf, 1. , 0.5 , 0.33333333, 0.25 ,\n",
" 0.2 , 0.16666667, 0.14285714, 0.125 , 0.11111111])"
]
},
"execution_count": 6,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"# Also a warning (but not an error) relating to infinity\n",
"1/arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 7,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([ 0, 1, 8, 27, 64, 125, 216, 343, 512, 729], dtype=int32)"
]
},
"execution_count": 7,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr**3"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Universal Array Functions\n",
"\n",
"NumPy comes with many [universal array functions](http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/ufuncs.html), or ufuncs, which are essentially just mathematical operations that can be applied across the array.
\n",
"___\n",
"Copyright Pierian Data\n",
"For more information, visit us at www.pieriandata.com"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"collapsed": true
},
"source": [
"# NumPy Operations"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Arithmetic\n",
"\n",
"You can easily perform *array with array* arithmetic, or *scalar with array* arithmetic. Let's see some examples:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 1,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])"
]
},
"execution_count": 1,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"import numpy as np\n",
"arr = np.arange(0,10)\n",
"arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 2,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([ 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18])"
]
},
"execution_count": 2,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr + arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 3,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([ 0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81])"
]
},
"execution_count": 3,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr * arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 4,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])"
]
},
"execution_count": 4,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr - arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 5,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stderr",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"C:\\Anaconda3\\envs\\tsa_course\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:3: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in true_divide\n",
" This is separate from the ipykernel package so we can avoid doing imports until\n"
]
},
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([nan, 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])"
]
},
"execution_count": 5,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"# This will raise a Warning on division by zero, but not an error!\n",
"# It just fills the spot with nan\n",
"arr/arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 6,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stderr",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"C:\\Anaconda3\\envs\\tsa_course\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:2: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in true_divide\n",
" \n"
]
},
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([ inf, 1. , 0.5 , 0.33333333, 0.25 ,\n",
" 0.2 , 0.16666667, 0.14285714, 0.125 , 0.11111111])"
]
},
"execution_count": 6,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"# Also a warning (but not an error) relating to infinity\n",
"1/arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 7,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([ 0, 1, 8, 27, 64, 125, 216, 343, 512, 729], dtype=int32)"
]
},
"execution_count": 7,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr**3"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Universal Array Functions\n",
"\n",
"NumPy comes with many [universal array functions](http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/ufuncs.html), or ufuncs, which are essentially just mathematical operations that can be applied across the array.
Let's show some common ones:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 8,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([0. , 1. , 1.41421356, 1.73205081, 2. ,\n",
" 2.23606798, 2.44948974, 2.64575131, 2.82842712, 3. ])"
]
},
"execution_count": 8,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"# Taking Square Roots\n",
"np.sqrt(arr)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 9,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([1.00000000e+00, 2.71828183e+00, 7.38905610e+00, 2.00855369e+01,\n",
" 5.45981500e+01, 1.48413159e+02, 4.03428793e+02, 1.09663316e+03,\n",
" 2.98095799e+03, 8.10308393e+03])"
]
},
"execution_count": 9,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"# Calculating exponential (e^)\n",
"np.exp(arr)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 10,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([ 0. , 0.84147098, 0.90929743, 0.14112001, -0.7568025 ,\n",
" -0.95892427, -0.2794155 , 0.6569866 , 0.98935825, 0.41211849])"
]
},
"execution_count": 10,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"# Trigonometric Functions like sine\n",
"np.sin(arr)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 11,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stderr",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"C:\\Anaconda3\\envs\\tsa_course\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:2: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log\n",
" \n"
]
},
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([ -inf, 0. , 0.69314718, 1.09861229, 1.38629436,\n",
" 1.60943791, 1.79175947, 1.94591015, 2.07944154, 2.19722458])"
]
},
"execution_count": 11,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"# Taking the Natural Logarithm\n",
"np.log(arr)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Summary Statistics on Arrays\n",
"\n",
"NumPy also offers common summary statistics like sum, mean and max. You would call these as methods on an array."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 12,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])"
]
},
"execution_count": 12,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr = np.arange(0,10)\n",
"arr"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 13,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"45"
]
},
"execution_count": 13,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr.sum()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 14,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"4.5"
]
},
"execution_count": 14,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr.mean()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 15,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"9"
]
},
"execution_count": 15,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr.max()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Other summary statistics include:\n",
"\n",
"arr.min() returns 0 minimum\n",
"arr.var() returns 8.25 variance\n",
"arr.std() returns 2.8722813232690143 standard deviation\n",
""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Axis Logic\n",
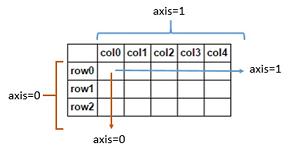
"When working with 2-dimensional arrays (matrices) we have to consider rows and columns. This becomes very important when we get to the section on pandas. In array terms, axis 0 (zero) is the vertical axis (rows), and axis 1 is the horizonal axis (columns). These values (0,1) correspond to the order in which arr.shape values are returned.\n",
"\n",
"Let's see how this affects our summary statistic calculations from above."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 16,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4],\n",
" [ 5, 6, 7, 8],\n",
" [ 9, 10, 11, 12]])"
]
},
"execution_count": 16,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr_2d = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]])\n",
"arr_2d"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 17,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([15, 18, 21, 24])"
]
},
"execution_count": 17,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr_2d.sum(axis=0)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"By passing in axis=0, we're returning an array of sums along the vertical axis, essentially [(1+5+9), (2+6+10), (3+7+11), (4+8+12)]\n",
"\n",
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"(3, 4)"
]
},
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr_2d.shape"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"This tells us that arr_2d has 3 rows and 4 columns.\n",
"\n",
"In arr_2d.sum(axis=0) above, the first element in each row was summed, then the second element, and so forth.\n",
"\n",
"So what should arr_2d.sum(axis=1) return?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"collapsed": true
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# THINK ABOUT WHAT THIS WILL RETURN BEFORE RUNNING THE CELL!\n",
"arr_2d.sum(axis=1)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# Great Job!\n",
"\n",
"That's all we need to know for now!"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.6.6"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 1
}
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"(3, 4)"
]
},
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr_2d.shape"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"This tells us that arr_2d has 3 rows and 4 columns.\n",
"\n",
"In arr_2d.sum(axis=0) above, the first element in each row was summed, then the second element, and so forth.\n",
"\n",
"So what should arr_2d.sum(axis=1) return?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"collapsed": true
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# THINK ABOUT WHAT THIS WILL RETURN BEFORE RUNNING THE CELL!\n",
"arr_2d.sum(axis=1)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# Great Job!\n",
"\n",
"That's all we need to know for now!"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.6.6"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 1
}
 \n",
"___\n",
"
\n",
"___\n",
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"(3, 4)"
]
},
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr_2d.shape"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"This tells us that arr_2d has 3 rows and 4 columns.\n",
"\n",
"In arr_2d.sum(axis=0) above, the first element in each row was summed, then the second element, and so forth.\n",
"\n",
"So what should arr_2d.sum(axis=1) return?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"collapsed": true
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# THINK ABOUT WHAT THIS WILL RETURN BEFORE RUNNING THE CELL!\n",
"arr_2d.sum(axis=1)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# Great Job!\n",
"\n",
"That's all we need to know for now!"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.6.6"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 1
}
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"(3, 4)"
]
},
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"arr_2d.shape"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"This tells us that arr_2d has 3 rows and 4 columns.\n",
"\n",
"In arr_2d.sum(axis=0) above, the first element in each row was summed, then the second element, and so forth.\n",
"\n",
"So what should arr_2d.sum(axis=1) return?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"collapsed": true
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# THINK ABOUT WHAT THIS WILL RETURN BEFORE RUNNING THE CELL!\n",
"arr_2d.sum(axis=1)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# Great Job!\n",
"\n",
"That's all we need to know for now!"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.6.6"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 1
}